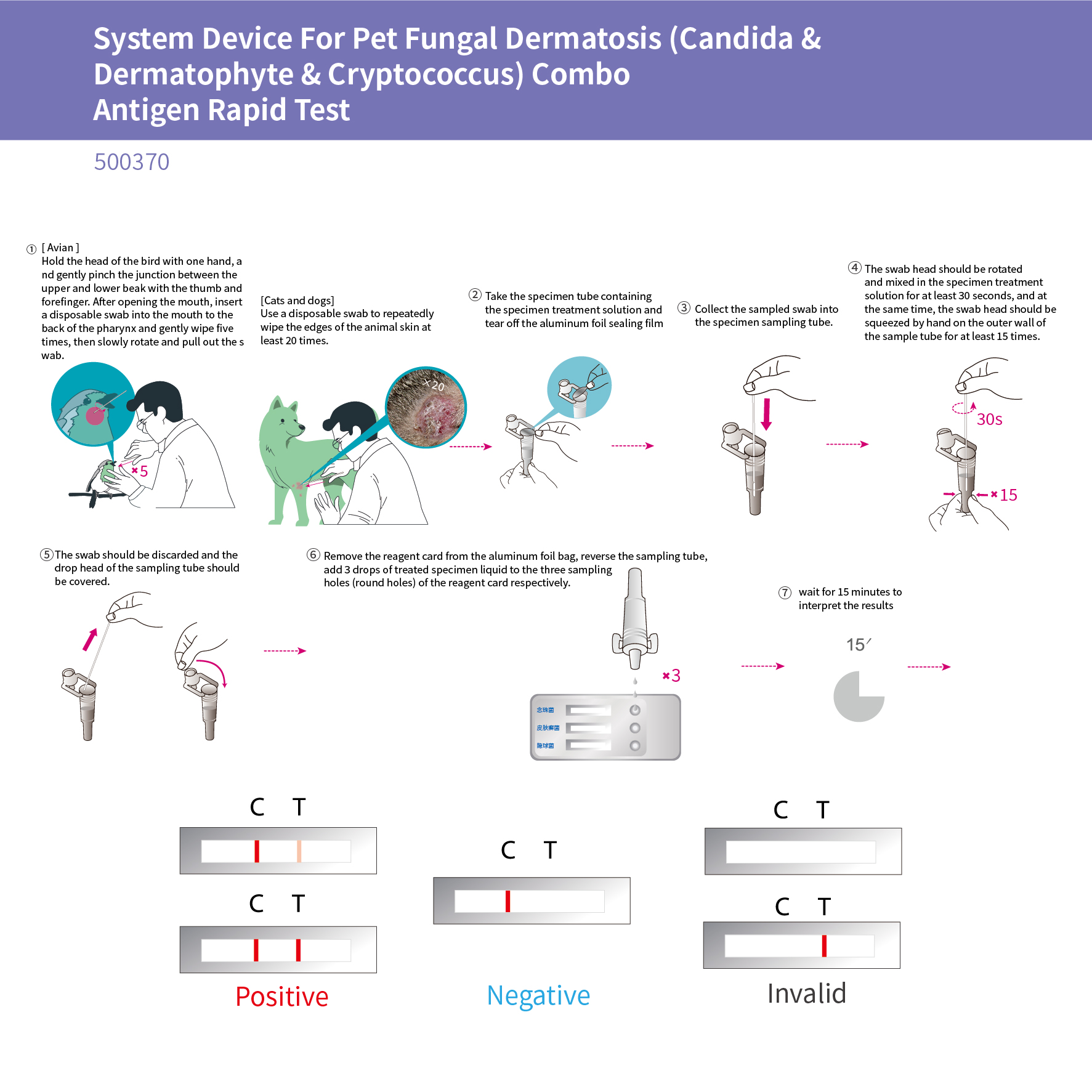
System Device For Pet Fungal Dermatosis (Candida & Dermatophyte & cryptococcus) Combo Antigen Rapid Test
This product is designed for the rapid screening of pet samples from cats, dogs and birds for Candida, Sphingomonas dermatitidis and Cryptococcus antigens, and can be used to assist in the diagnosis of Candida, Sphingomonas dermatitidis and Cryptococcus infections in pets.
Dermatological diseases are common in cats, dogs and birds, and Candida, S. dermatitidis and Cryptococcus are the most common fungi causing dermatological diseases in pets.
Candida infects the oral mucosa, oesophagus and crop of birds. The main symptoms are anorexia, crop obstruction, oral leukoplakia, food reflux and weight loss. Candida infections can occur in dogs and cats with chronic illnesses such as diabetes, kidney disease, or antibiotic use. Candida infections in dogs and cats include skin infections, oral and respiratory mucosal infections, intestinal infections, and urinary tract infections. Candida oral infections can cause fungal stomatitis, intestinal infections can cause diarrhoea and blood in the stool, and urinary tract infections can cause difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. Ultrasound testing will also often observe fungal clumps in the bladder.
Dermatophytes infect the skin of dogs and cats, causing superficial skin infections. The asexual stage of dermatophytes belongs to the subphylum Hemiptera and the sexual stage belongs to the subphylum Ascomycota. Dermatophytes can be classified into three genera based on the characteristics of the macroconidia. Trichophyton: rod-shaped macroconidia; Microsporum: shuttle-shaped macroconidia; and Epidermophyton: pestle-shaped macroconidia. In pet dermatophytosis, Microsporum canis is the most common causative agent.
Cryptococcus infects a wide range of animals and is a systemic fungal infection. It primarily affects the respiratory tract, eyes, skin, and central nervous system. Cryptococcus usually presents on the skin as papules, pustules, nodules and ulcers.
There are many causes of dermatological disease in pets, and prompt swabbing of lesions is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The current use of latex immunochromatography to detect pathogens allows rapid screening for suspected Candida, Tinea versicolor, and Cryptococcus infections in pets and facilitates early diagnosis and treatment of pet skin diseases.