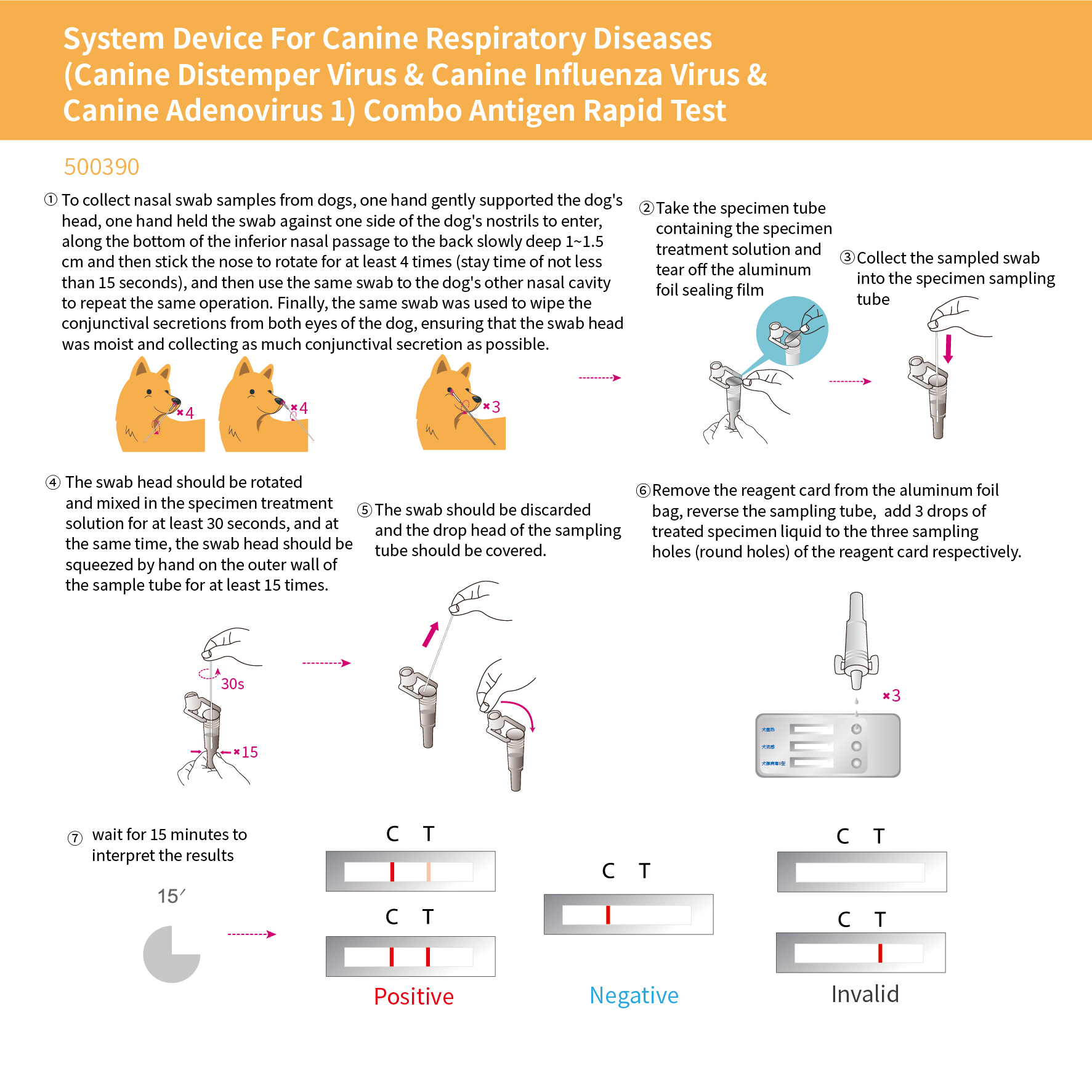
System Device For Canine Respiratory Diseases (Canine Distemper Virus & Canine Influenza Virus & Canino Adenovirus 1) Combo Antigen Rapid Test
This product is designed for rapid screening of canine distemper virus (CDV), canine influenza virus (CIV) and canine adenovirus type II (CAVII) antigens in ocular and nasal secretion samples from dogs, and can be used as an aid in the diagnosis of CDV, CAVII and CAVII infections.
Canine infectious respiratory disease is a common disease in dogs, in which canine distemper virus, canine influenza virus and canine adenovirus type II are the common pathogens causing canine respiratory disease.
Canine distemper is a highly contagious and widespread disease of dogs and other carnivores. Canine distemper virus belongs to the measles virus genus and causes systemic infections throughout the body. Transmission is mainly by aerosol or direct contact. The incubation period after infection is short, with a mortality rate of about 50 per cent. It spreads rapidly in puppies, especially those aged 3-6 months. The incubation period is usually about 1 week. The initial increase in temperature of biphasic fever is not easy to detect, and when the temperature rises for the second time, the symptoms of ocular and nasal discharge, inflammation and enlarged tonsils are obvious. Coughing, vomiting and diarrhoea are usually secondary to infection. A red rash and pustules may appear on the abdomen. Acute cases may last for several weeks or develop neurological symptoms leading to death. Common neurological symptoms include paralysis, clonus and seizures.
Canine influenza virus (CIV) is a large infectious respiratory disease virus that spreads rapidly in dogs, causing clinical signs of respiratory distress such as coughing, runny nose, sneezing, fever, dyspnoea, with or without coughing up sputum, depression, loss of appetite, and ocular and nasal discharge, which may progress to pneumonia. Dogs infected with this virus usually have a mild onset of symptoms, with a persistent cough that may last up to three weeks, and yellow nasal discharge. More serious symptoms of dog flu include high fever, increased respiratory rate, and other pneumonia-like symptoms.
There are two serotypes of canine adenovirus. Type I can cause both canine infectious hepatitis and type II can cause canine infectious laryngotracheitis and enteritis. Type II is commonly found in puppies, especially in newly weaned litters, and the disease can cause litter morbidity and high mortality in puppies under 4 months of age. Canine adenovirus type II is readily transmitted by aerosols, replicates in the upper and lower respiratory tract, and is a highly contagious disease. Infected dogs show clinical signs similar to canine infectious tracheobronchitis (kennel cough), with persistent high fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, muscle tremors, cyanosis of the visible mucous membranes, and in some cases vomiting, diarrhoea, tonsillitis, laryngotracheitis and pneumonia. The infection can be carried for a long time and can occur in any season. Most dogs recover and develop immunity.
Canine infectious respiratory disease is difficult to determine from the clinical signs that the infection is caused by a particular pathogen, mainly because many of the symptoms are superimposed and are not specific. The main diagnostic methods for canine infectious respiratory diseases are serological methods for detecting viral antibodies and PCR methods for detecting DNA, RNA viruses and bacteria of various pathogens, but since many dogs are vaccinated, the antibody level obtained from serological experiments cannot correctly respond to the actual infection situation of the dog, and the PCR method requires specialised technicians, venues, and equipments, and is time-consuming. The current use of latex immunochromatography to detect pathogens allows rapid screening for suspected canine distemper virus infection, canine influenza virus infection and canine adenovirus type II infection, which is conducive to early diagnosis and treatment of canine diseases.