One world one fight
─International cooperation to build a global community of common destiny responding to COVID-19 pandemic challeng
The novel coronavirus sweeping across the world has resulted in an ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic crisis. The novel coronavirus has no borders, no country will be spared from this battle against COVID-19. In response to this worldwide COVID-19 pandemic, Liming Bio-Products Corp is making contributions to support the well-being of our global communities.
Our world is currently faced with the unprecedented impact of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. To date, there is no efficient drug available for the treatment of this disease. However, many diagnostic tests have been developed for the detection of COVID-19. These tests are based on molecular or serological methods to detect the novel coronavirus specific nucleic acid or antibody biomarkers. As COVID-19 has reached a pandemic status, early diagnosis of the novel coronavirus infection is critical in assessing the spread of the virus and containing it, but a perfect test for universal use does not yet exist. We have to know what tests could potentially be used for screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of the COVID-19 infection, and what are their limitations. It is very important how to make better use of these scientific tools and to help identify and control the emergence of this rapidly spreading and serious illness.
The purpose of the detection of the novel coronavirus is to determine whether an individual who has COVID-19 infection or an asymptotic carrier who may spread the virus silently, to provide essential information to guide decision-making for clinical treatment. Previous studies have shown that 70% of clinical decisions depend on the testing results. When different detection methods are used, the requirements of the detection reagent kits are also different.
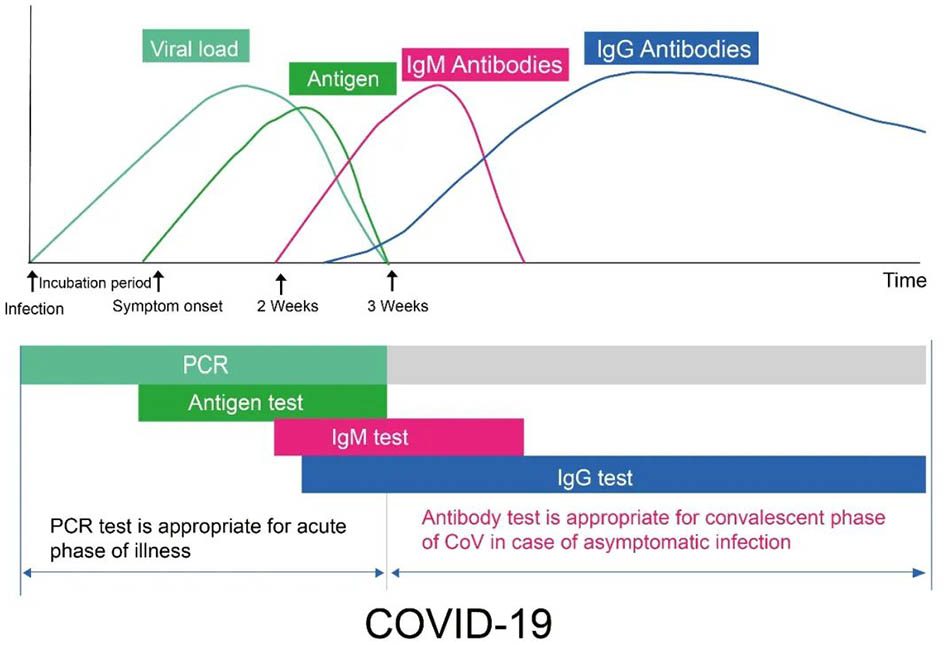
Figure 1
Figure1: Diagram showing the key stages of general biomarker levels during the typical time course of COVID-19 infection. The X-axis indicates the number of days of infection, and the Y-axis indicates the viral load, concentration of antigens, and concentration of antibodies in different periods. Antibody refers to IgM and IgG antibodies. Both RT-PCR and antigen detection are used to detect the presence or absence of novel coronavirus,which is direct evidence for early patient detection. Within a week of viral infection, PCR detection, or antigen detection is preferred. After the novel coronavirus infection for about 7 days, the IgM antibody against the novel coronavirus has gradually increased in the patient's blood, but the duration of the existence is short, and its concentration decreases quickly. In contrast, the IgG antibody against the virus appears later, usually about 14 days after the virus infection. The IgG concentration gradually increases, and it persists a long period in the blood. Thus, if the IgM is detected in the patient's blood, it means that the virus has recently infected,which is an early infection marker. When the IgG antibody is detected in the patient's blood, it means that the viral infection has been for some time. It is also called late infection or previous infection. It is often seen in patients who are in the recovery phase.
The biomarkers of novel coronavirus
The novel coronavirus is an RNA virus, which is composed of proteins and nucleic acids. The virus invades the host (human)body, enters cells through binding site corresponding receptor ACE2, and replicate in host cells, causing the human immune system to respond to foreign invaders and produce specific antibodies. Therefore, the vial nucleic acids and antigens,and specific antibodies against novel coronavirus can theoretically be used as specific biomarkers for the detection of the novel coronavirus. For nucleic acid detection, RT-PCR technology is the most commonly used, while serological methods are commonly used for the detection of the novel coronavirus-specific antibodies. Currently, there are a variety of test methods available that we can choose for testing COVID-19 infection [1].
Basic principles of main test methods for novel coronavirus
Many diagnostic tests for COVID_19 are available so far, with more test kits receiving approval under an emergency use authorization every day. Although the new test developments coming out with so many different names and formats, all of the current COVID_19 tests basically rely on two major technologies: nucleic acid detection for the viral RNA and serological immunoassays that detect viral-specific antibodies (IgM and IgG).
01. Nucleic acid detection
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are the common nucleic acid methods for the detection of novel coronavirus RNA. RT-PCR is the first type of test for COVID-19, recommended by both the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
02.Serological antibody detection
Antibody is a protective protein produced in human body in response to the virus infection. The IgM is an early type of antibody whereas IgG is a later type antibody. The serum or plasma sample is usually examined for the presence of specific IgM and IgG types of the antibody for assessment of acute and convalescent phases of COVID-19 infection. These antibody-based detection methods include colloidal gold immunochromatography assay, latex or fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and chemiluminescence assay.
03.Viral antigen detection
Antigen is a structure on the virus recognized by the human body that triggers the immune defense system to produce antibodies to clear the virus from blood and tissues. A viral antigen present on the virus can be targeted and detected by using immunoassay. Like viral RNA, viral antigens are also present in the respiratory tract of infected individuals and can be used to diagnose acute-phase of the COVID-19 infection. Therefore, it is often recommended to collect upper respiratory specimens such as saliva, nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs, deep cough sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid(BALF) for initial antigen testing.
Selecting of testing methods for novel coronavirus
Selecting a testing method involves many factors, including clinical setting, testing quality control, turnaround time,testing costs, sampling collection methods, laboratory personnel technical requirements, facility and equipment requirements. The detection of nucleic acids or viral antigens is to provide direct evidence of the presence of the viruses and confirm the diagnosis of novel coronavirus infection. Although there are many methods for antigen detection, their detection sensitivity of the novel coronavirus is theoretically lower than that of the RT-PCR amplification. Antibody testing is the detection of anti-virus antibodies produced in the human body, which is lagging in time and often cannot be used for early detection during the acute phase of virus infection. The clinical setting for detection applications can vary, and the sample collection sites may also be different. For the detection of viral nucleic acids and antigens, the specimen needs to be collected in the respiratory tract where the virus is present, such as nasopharyngeal swabs, oropharyngeal swabs, sputum, or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). For antibody-based detection, blood specimen needs to be collected and examined for the presence of specific anti-virus antibody (IgM/IgG). However, antibody and nucleic acid test results can complement each other. For example, when the testing result is the nucleic acid-negative, IgM-negative but IgG-positive, these results indicate that the patient does not currently carry the virus, but has been recovered from the novel coronavirus infection. [2]
Advantages and disadvantages of novel coronavirus tests
In the Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version7) (Released by National Health Commission & State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine on March 3, 2020), nucleic acid testing is used as the gold standard method for the diagnosis of the novel coronavirus infection,while antibody testing is also considered as one of the confirmation methods for the diagnosis.

Pathogenic and serological findings
(1) Pathogenic findings: Novel coronavirus nucleic acid can be detected in nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, lower respiratory tract secretions, blood, feces and other specimens using RT-PCRand/or NGS methods. It is more accurate if specimens are obtained from lower respiratory tract (sputum or air tract extraction). The specimens should be submitted for testing as soon as possible after collection.
(2) Serological findings: NCP virus specific IgM becomes detectable around 3-5 days after onset; IgG reaches a titration of at least 4-fold increase during convalescence compared with the acute phase.
However, the selection of testing methods depends on geographic locations, medical regulations, and clinical settings. In the USA, the NIH issued Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines (Site Updated: April 21,2020 ) and FDA issued Policy for Diagnostic Tests for Coronavirus Disease-2019 during the Public Health Emergency (issued on March 16,2020), in which serological testing of the IgM/IgG antibodies selected only as a screening test.
Nucleic Acid Detection Method
RT_PCR is a highly sensitive nucleic acid test designed to detect whether or not the novel coronavirus RNA is present in the respiratory or other specimen. A positive PCR test result means the presence of novel coronavirus RNA in the sample to confirm the COVID-19 infection. A negative PCR test result does not mean the absence of the virus infection because it could be affected by poor sample quality or disease time point at the recovered phase,etc. Although RT-PCR is a highly sensitive test, it has several drawbacks. RT-PCR tests can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, crucially dependent on the high quality of the sample. This can be a challenge because the amount of viral RNA not only varies tremendously between different patients but also can vary within the same patient depending on the time points when the sample is collected as well as the infection phases or the onset of clinical symptoms. Detecting the novel coronavirus requires high-quality specimens that contain a sufficient amount of intact viral RNA.
The RT-PCR test may give an incorrect negative result (false negative) for some patients who have COVID-19 infection. As we know, the main infection sites of the novel coronavirus are located at the lung and the lower respiratory tract, such as alveoli and bronchi. Therefore, the sputum specimen from a deep cough or the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) considered to have the highest sensitivity for viral detection. However, in clinical practice, samples are often collected from the upper respiratory tract by using nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs. Collecting these specimens is not only uncomfortable for patients but also requires specially trained personnel. To make sampling less invasive or easier, in some cases the patients may be given an oral swab and allow them to take a sample from the buccal mucosa or tongue swabbing themselves. Without sufficient viral RNA, RT-qPCR can return a false-negative test result. In Hubei province, China, RT-PCR sensitivity in the initial detection was reported only about 30%-50%, with an average of 40%. The high rate of false-negative was most likely caused by insufficient sampling.
In addition, the RT-PCR test requires highly trained personnel to perform complex RNA extraction steps and PCR amplification procedure. It also requires a higher level of biosafety protection, special laboratory facility, and real-time PCR instrument. In china, the RT-PCR test for COVID-19 detection needs to be performed in biosafety level 2 laboratories(BSL-2), with personnel protection using biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) practice. Under these requirements, from the beginning of January to early February 2020, the capacity of China Wuhan's CDC laboratory was only able to detect a few hundred cases per day. Normally, this would not be a problem when testing other infectious diseases. However, when dealing with a global pandemic such as COVID-19 with potentially millions of people to be tested, RT-PCR becomes a critical issue due to its requirements for special laboratory facilities or technical equipment. These disadvantages may limit the RT-PCR to be used as an efficient tool for screening, and also may lead to delays in the reports of testing results.
Serological antibody detection method
With the progress of the disease course,especially in the middle and late stages, the antibody detection rate is very high. A study in Wuhan Central South Hospital showed that the antibody detection rate could reach more than 90% in the third week of COVID-19 infection. Also, the antibody is the product of the human immune response against the novel coronavirus. The antibody test offers several advantages over RT-PCR. Firstly, the serological antibody tests simple and rapid. Antibody lateral flow tests can be used for point-of-care to deliver a result in 15 minutes. Secondly, the target detected by the serological test is the antibody,which is known to be much more stable than viral RNA. During collection, transport, storage and testing, the specimens for antibody tests are generally more stable than the specimens for RT-PCR. Thirdly, because the antibody is evenly distributed in the blood circulation, there is less sampling variation compared to the nucleic acid test. The sample volume required for the antibody test is relatively small. For example, 10 microliter of finger-prick blood is sufficient for use in the antibody lateral flow test.
In general, the antibody test is chosen as a supplement tool for nucleic acid detection to improve the detection rate of the novel coronavirus during the disease courses. When the antibody test is used together with a nucleic acid test, it may increase assay accuracy for the diagnosis of COVID19 by reducing potential false-positive and false-negative results. The current operation guide does not recommend using two types of test separately as an independent detection format but should be used as a combined format. [2]
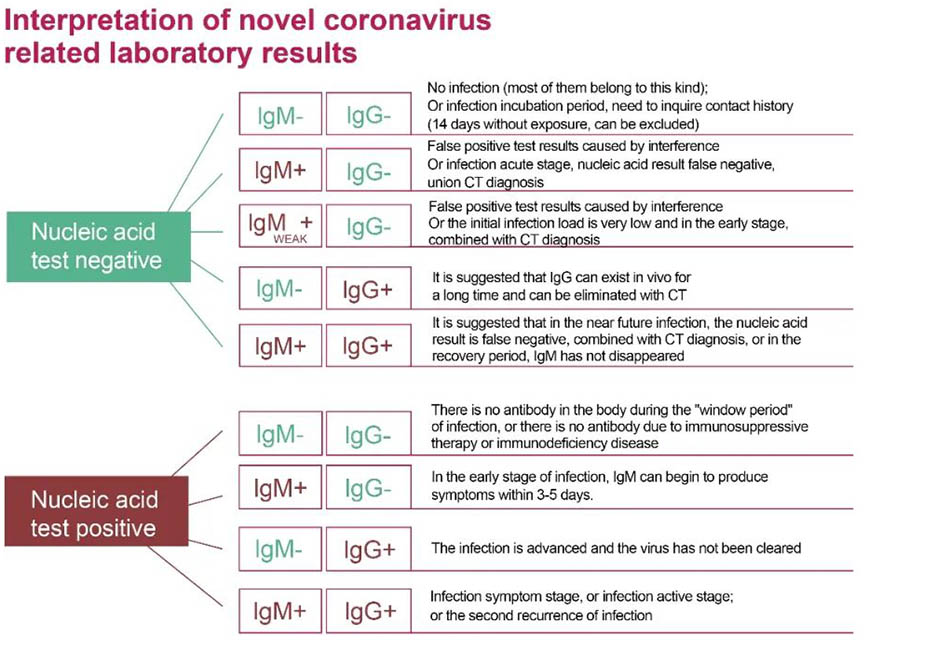
Figure2: The correct interpretation of nucleic acid and antibody test results for the detection of novel coronavirus infection

Figure 3: Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. – Novel coronavirus IgM/IgG antibody dual rapid test Kit (StrongStep® SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG Antibody Rapid Test, Latex Immunochromatography)

Figure 4: Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. – StrongStep® Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Multiplex Real-Time PCR kit (detection for three genes, fluorescent probe method).
Note: This highly sensitive, ready-to-use PCR kit is available in lyophilized format (freeze-drying process) for long-term storage. The kit can be transported and stored at room temperature and is stable for one year. Each tube of premix contains all of the reagents needed for the PCR amplification, including Reverse-transcriptase, Taq polymerase, primers, probes, and dNTPs substrates.Users can simply reconstitute the mix by adding PCR-grade water along with the template and then load onto a PCR instrument to run the amplification.
In response to the novel coronavirus outbreak, Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. has worked rapidly to develop two diagnostic kits to enable clinical and public health laboratories to quickly diagnose COVID-19 infection. These kits are very suitable for use for large-scale screening in countries and regions where the novel coronavirus outbreak is rapidly spreading, and for providing diagnosis and confirmation for COVID-19 infection. These kits are for use only under Pre-notified Emergency Use Authorization (PEUA). Testing is limited to laboratories certified under the regulations of the national or local authorities.
Antigen detection method
1. Viral antigen detection is classified in the same category of direct detection as nucleic acid detection. These direct detection methods look for evidence of viral pathogens in the specimen and can be used for confirmation diagnosis. However, the development of antigen detection kits requires high quality of monoclonal antibodies with strong affinity and high sensitivity capable of recognizing and capturing pathogenic viruses. It usually takes more than six months to select and optimize a monoclonal antibody suitable for use in the preparation of the antigen detection kit.
2. Currently, the reagents for direct detection of the novel coronavirus are still under research and development stage. Therefore, no antigen detection kit has been clinically validated and commercially available. Although it was previously reported that a diagnostic firm in Shenzhen has developed an antigen detection kit and clinically tested in Spain, the assay reliability and accuracy could not be validated due to the presence of reagent quality issues. To date, NMPA (former China FDA) has not approved any antigen detection kit for clinical use yet. In conclusion, a variety of detection methods have been developed. Each method has its advantages and limitations. The results from different methods can be used for verification and complement.
3. Producing a quality COVID-19 test kit strongly depends on optimization during research and development. Liming Bio-Product Co.,Ltd. test kits are required to meet stringent manufacturing and quality control standards to ensure that they provide the highest levels of performance and consistency. The scientists at Liming Bio-Product Co., Ltd. have over twenty years’ experience in designing, testing, and optimizing in vitro diagnostic kits to ensure the highest level of performance in analytical quantification.
During the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Chinese government faced surge of the huge demand for epidemic prevention materials in the international hotspots. On April 5, at the press conference of the State Council Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism "Strengthening the Quality Management of Medical Materials and Regulating the Order of the Market", Jiang Fan, a first-level inspector of the Foreign Trade Department of the Ministry of Commerce, said, "Next, we will focus our efforts on two aspects, first, to speed up the support of more medical supplies needed by the international community, and also, to improve quality control, regulation, and management of the products. We will make China's contribution to jointly responding to the global epidemic and building a community with a shared future for mankind.



Figure 5: Liming Bio-Products Co.,Ltd.'s novel coronavirus reagent has obtained the EU CE registration certificate
The honorary certificate


Houshenshan
Figure 6. Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. supported Wuhan Vulcan(HouShenShan) Mountain Hospital to fight against the COVID-19 epidemic and was awarded the honorary certificate of Wuhan Red Cross. Wuhan Vulcan mountain hospital is the most famous hospital in China that specializes in the treatment of severe COVID - 19 patients.
As the novel coronavirus outbreak continues spreading around the world, Nanjing Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. Is stepping up to support and help communities worldwide with our innovative technologies to fight this unprecedented global threat. Rapid testing of COVID-19 infection is a critical part of addressing this threat. We continue to contribute in a significant way by providing high-quality diagnostic platforms into the hands of frontline healthcare workers so people can receive the critical testing results they need. Liming Bio-products Co., Ltd.'s efforts in the battle against COVID-19 pandemic are to contribute our technologies, experiences, and expertise to international communities for the construction of a global community of destiny.
Long Press~Scan and Follow Us
Email: sales@limingbio.com
Website: https://limingbio.com
Post time: May-01-2020







