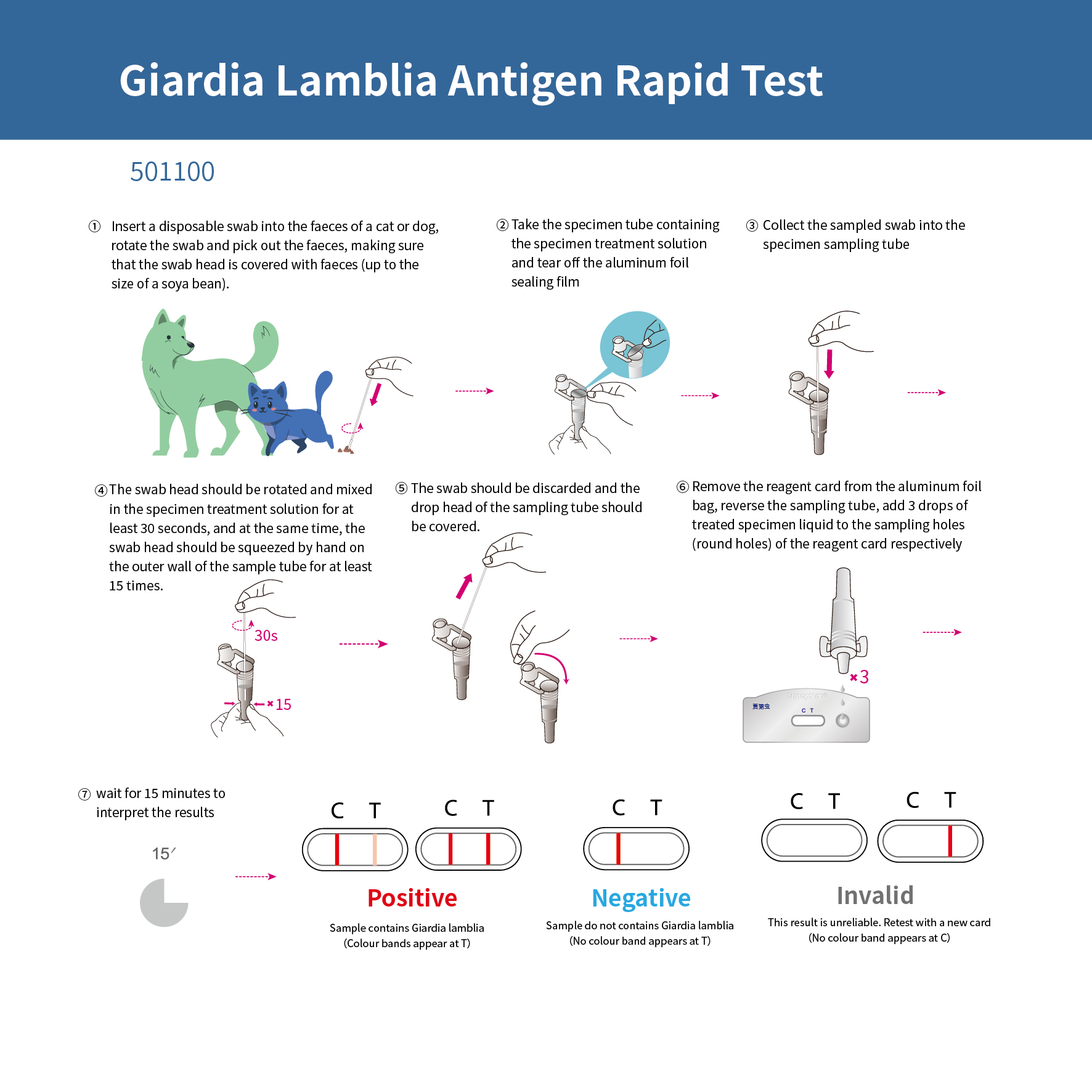
Giardia Lamblia Antigen Rapid Test
This product is used for rapid screening of pet dog and cat faecal samples for Giardia lamblia antigen, and can be used as an aid in the diagnosis of Giardia lamblia.
Giardia lamblia, also known as giardiasis, is a protozoan disease caused by Giardia lamblia parasites in the small intestine and is a zoonotic disease that can be transmitted between humans and animals. Giardia lamblia can survive for 2-3 months in raw, cold water or soil and prefers a moist, cold environment. Pet dogs and cats can cause Giardia if they ingest contaminated water or food, or come into contact with the faeces of other infected animals, or lick themselves after coming into contact with contaminated surfaces (e.g., grass, bins, etc.).
Infected dogs and cats mainly exhibit diarrhoea, but there are also cases of latent infection without clinical symptoms. Symptoms usually appear 5-10 days after infection with Giardia, such as jellied loose faeces (which may contain mucus or blood) or soft, light yellow stools; they may also show signs of depression, loss or elimination of appetite, roughness of the coat, flatulence, lethargy, anaemia, vomiting, etc. If left untreated, persistent diarrhoea may occur. If not treated in time, persistent diarrhoea or blood in the stools will occur, and even secondary canine distemper, microvirus and other malignant infectious diseases, threatening to threaten the lives of young pets.
Direct stool smear microscopy is commonly used in clinical practice, where a smear is made from fresh paste or watery stool with saline and examined microscopically. There is also the Diff-Quick C staining method in which a small amount of watery stool is mixed with a small amount of Diff-Quick C and made into a smear for microscopic examination. There are also enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, indirect fluorescent antibody techniques, convective immunoelectrophoresis and spot immunobinding tests. All of these methods require specialised personnel and equipment. The current use of latex immunochromatography for the detection of Giardia lamblia antigen in faeces allows rapid screening for suspected Giardia lamblia infection.