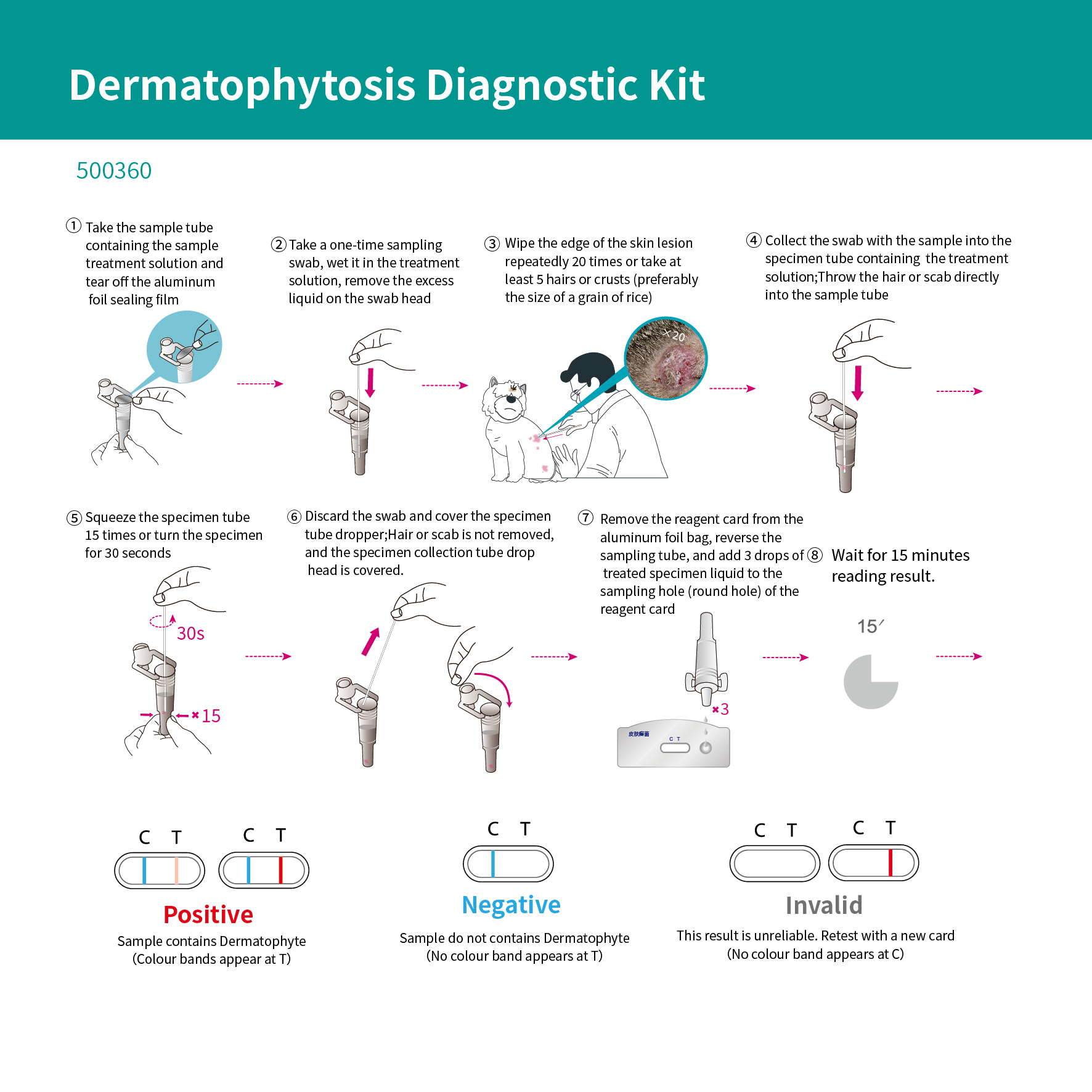
Dermatophytosis Diagnostic Kit
The asexual stage of dermatophytes belongs to the subphylum Hemiptera and the sexual stage belongs to the subphylum Ascomycota. Based on the characteristics of the macroconidia, dermatophytes can be divided into three genera. Trichophyton: rod-shaped macroconidia; Microsporum: spindle-shaped macroconidia; and Epidermophyton: pestle-shaped macroconidia. In dermatophytosis, Trichophyton rubrum is the most common causative agent, accounting for 88.19%, the others being, in order of prevalence, Trichophyton mentagrophytes (6.77%) and Microsporum canis (3.33%). Less common are Epidermophyton floccosum (0.89%), Microsporum gypseum (0.49%), and Trichophyton violaceum (0.32%). Dermatophytes mainly invade the skin, hair and finger (toe) nails of humans or animals, and parasitize or rot in the keratin tissue of the epidermis, hair and nail plate, causing tinea corporis and tinea pedis in humans or animals.
The main components of fungal cell walls are chitin, glucan, cellulose, and mannan. Mannans are mostly found in fungal cell walls as α-1,6-mannan as a backbone chain. Mannans can be secreted on the skin of the host and are substances that attenuate the immune response and have the function of adsorbing pathogenic bacteria and regulating immunity. The structure of α-1,6-mannan varies greatly among different fungi, and the structure of α-1,6-mannan that causes tinea versicolor in pets is very specific, so α-1,6-mannan can be used as a target for the detection of tinea versicolor in pets. The Pet Dermatophytosis Diagnostic Kit (Latex Immunochromatography) uses immunochromatographic techniques to qualitatively detect the presence of α-1,6-mannan in samples.